These methods of birth prevention are “natural” because they are not mechanical and not a result of hormone manipulation. Instead, these measures need that a man and woman do not have sexual intercourse throughout the time when an egg is available to be fertilized by a sperm.
The fertility awareness methods (FAMs) are primarily based upon identifying when a woman ovulates each month. To use a FAM, it is necessary to identify for signs and symptoms that specify ovulation has occurred or is about to occur. Approximately the egg is released about 14 days before a woman’s next menstrual period, But because the egg survives 6 to 24 hours after ovulation and the sperm can live 48 to 72 hours, the actual time during which a woman may pregnant is measured not in hours, not in days, but weeks.
FAMs can be up to 98% effective, but they require continuous and conscious commitment with considerable monitoring and self-control.
Natural methods of contraception are:
- Calendar rhythm method
- Basal body temperature method
- Mucus inspection method
- Symptothermal method
- Ovulation indicator testing kits
- Withdrawal method
- Lactational infertility
- Douching and urination
1. CALENDAR RHYTHM METHOD
The calendar rhythm method relies upon calculating a woman’s fertile phase on the calendar based on her 12 previous menstrual cycles, a woman subtracts 18 days from her shortest menstrual cycle to determine her initial fertile day and 11 days from her longest menstrual cycle to spot her last fertile day. She can then determine the total number of days throughout that she may ovulate. If a woman’s menstrual cycle is quite irregular from month to month, there will be a greater number of days during which she might become pregnant. The calendar method is almost 80% effective as a contraceptive and when used alone is considered outdated
2. BASAL BODY TEMPERATURE (BBT) METHOD
The basal body temperature method corresponds on the fact that a woman’s temperature reduces 12 to 24 hours before an egg is withdrawn from her ovary and then increases again once the egg has been released. Unfortunately, this temperature difference is minute, it is mostly less than 1 degree F in the body at rest
The basal temperature method requires that a woman take her temperature early morning before she gets out of bed. A special thermometer can be used, that is more accurate and sensitive than a typical oral thermometer and the daily temperature variation is carefully noted. This must be done every month. Online calculators are available to her as a woman to chart her basal body temperature. To use the basal body temperature as a birth preventing method, a woman should abstain from having sexual intercourse from the time of her temperature decreases until at least 48 to 72 hours following her temperature rises again.
3. MUCUS INSPECTION METHOD (Billings method)
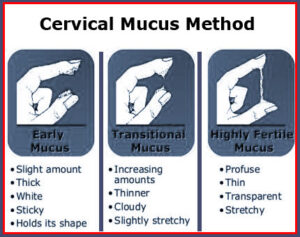
The mucus inspection method is observing the presence or absence of cervical mucus that a woman produces in response to estrogen. A woman will generate a larger amount of more watery mucus than usual (like raw white) just before releasing an egg from her ovary. This mucus stretches for up to an inch when pulled apart. A woman should examine differences in the quantity and quality of her cervical mucus by verifying its appearance on her pads, underwear, and toilet tissue or she may gently take a sample of mucus from her vaginal opening using two fingers. She may choose to have sexual intercourse between the time of her last menstrual period and the time of change in the cervical mucus. During this period, it is recommended that she can have sexual intercourse only every other day because the presence of seminal fluid from a man makes it more trouble to identify the nature of her cervical mucus. If the woman does not want to become pregnant, she should not have sexual intercourse at all for 3 to 4 days once she notices the change in her cervical mucus.
4. SYMPTOTHERMAL METHOD
This method is the combination of the above-described calendar, basal body temperature, and the mucus inspection method. Not only are all these factors are taken into consideration but also consider other symptoms like breast tenderness and slight cramping. Some women may experience lower abdominal discomfort during the release of an egg.
5. OVULATION INDICATOR TESTING KITS
This is a special kit that measures the number of luteinizing hormones (LH) in the urine so that the woman can use this kit to determine when she is most expected to ovulate. Because the Luteinizing hormone promotes the maturation of the egg in the ovary. The amount of LH mostly increases 20 to 48 hours prior to ovulation. This is mean by LH surge, this can be identified in women urine 8 to 12 hours later.
There are many types of Ovulation prediction kits are available in the market which ranges from simple to complex. In the simplest, the woman can urinate onto the test stick and the amount of LH is verified by the change in colour. The intensity of the colour is relating to the amount of LH in the urine. A woman starts to testing her urine 2 to 3 days before she expects to ovulate based on the dates of her previous monthly cycles.
The optimum days for fertilization are two days prior to ovulation, the day of ovulation, and two days after ovulation. The high risk of becoming pregnant is if the intercourse occurs within 24 hours after the LH surge. Ovulation prediction kits are mostly used to make women aware that she is about ovulation and should take appropriate contraceptive precautions.
6. WITHDRAWAL METHOD (COITUS INTERRUPTUS)
In this method, the man withdraws his penis from the woman’s vagina during the sexual intercourse before he ejaculates, so that the sperm released from his penis does not enter his vagina. This is the most common method but it affects the pleasure during intercourse. There are problems with using withdrawal as a birth preventive measure. Firstly, a man may releases sperm before he has an orgasm. Furthermore, a man requires self-control and an accurate sense of timing to be able to withdraw his penis from the woman’s vagina before ejaculation. Sometimes it may be difficult for a man to do successfully.
7. LACTATIONAL INFERTILITY
Lactational infertility is related to the fact that a woman cannot become pregnant as long as she is breastfeeding her baby. Indeed, a woman may not ovulate quite as soon as giving birth to a child and she may conceive if she were not breastfeeding. Women who are breastfeeding usually start ovulating again between 10 to 12 weeks after delivery.
Nursing women may start ovulating again and not realize she is fertile, as ovulation can occur prior to the return of her menstrual period. If this occurs and the mother has unprotected sexual intercourse, she will be able to become pregnant at the constant time she continues to be breastfeeding her baby.
8. DOUCHING AND URINATION
Vaginal douching is the method of using a liquid solution to wash out mucus and other types of bodily debris from a women’s vagina. Many women choose to make regular douching as part of their routine for maintaining vaginal hygiene. This is not a 100% successful method of birth control. During intercourse, active sperm can reach a woman’s cervix and even the upper part of the uterus within five minutes of ejaculation. Douching soon after intercourse cannot provide enough contraceptive benefits, and the douching could even force sperm higher up into the uterus. Besides if a woman douches within a 6 to 8 hours period after using spermicide, she may reduce the effectiveness of this contraceptive method.
Some women used to think that standing up and urinating immediately after sexual intercourse might reduce the possibilities of them becoming pregnant. They think that gravity might make it more struggle for sperm to swim uphill towards the uterus and that the stream of urine running over their vagina area would wash away sperms, similar to douching. However, douching and urination after intercourse do not have any contraceptive value.
Advantages of natural contraceptive methods
- Safe: Natural birth control methods are useful in avoiding risks and side effects that come with contraceptive drugs or devices.
- No need for any device
- Pleasure: Unlike condoms, sponges, copper T, etc, With natural contraceptive methods, there is no barrier hence, love-making is sensual and satisfying.
- No expenses like condoms, pills, and other barrier methods
- No hormonal or surgical involvement with the body
Disadvantages of natural contraceptive methods
- Required careful observations
- it doesn’t protect the couples from any type of sexually transmitted diseases (STD)
- Couples required to train themselves to get more accurate readings
- May chance of time-consuming and frustrating
- High chance of inaccurate readings because of stress and lifestyle
- Not suitable for women with irregular menstrual period
Precautions to take while using a natural method of contraception
- You have to keep a record of your menstrual cycles regularly
- If you currently stop taking any type of birth control or contraceptive pills, there is a high chance of irregular menstruation for a few months
- If your menstrual cycle is irregular and having unprotected sex, you have a high chance of ending up with a pregnancy